Chemical probe can regulate signaling pathway and block cell invasion by arboviruses
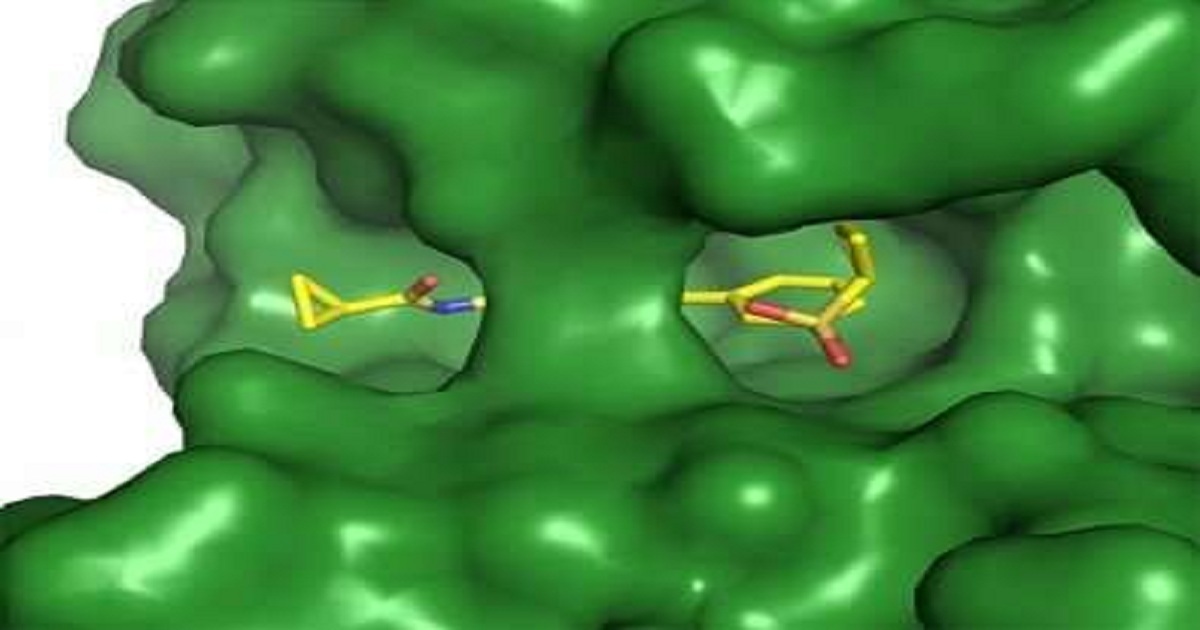
Cells in humans and other vertebrates, as well as invertebrates, have signaling pathways that play essential roles in embryo development, cell proliferation and tissue structuring. Dysregulation in one of these signaling pathways, known as the beta-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling pathway, can cause embryo malformation and diseases such as breast cancer and cervical cancer. Researchers at the Center for Medicinal Chemistry (CQMED) have discovered a way to regulate this pathway. Created with support from São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP through its Research Partnership for Technological Innovation program (PITE), CQMED is a unit of the Brazilian Agency for Industrial Research and Innovation (EMBRAPII) that specializes in biopharmaceuticals and pharmaceuticals, comprising researchers from the University of Campinas's Center for Molecular Biology and Genetic Engineering (CBMEG) and the same university's Biology Institute (IB-UNICAMP).